In part 1 I outlined the rationale for the project and my plans for structuring the project using a three-layered architecture. Today's post will focus on my project set-up workflow.
Project Set-up
-
Create a new virtual environment for the project and upgrade pip, setuptools and wheel.
esd/$ python -m venv .venv --prompt . esd/$ source .venv/bin/activate (esd) esd/$ python -m pip install -U pip setuptools wheel -
Initiate a git repository in the project directory for version control and add a
.gitignorefile. Add the.venvdirectory to the.gitignorefile to avoid committing the virtual environment to version control.(esd) esd/$ git init (esd) esd/$ echo .venv > .gitignore -
Install
pip-toolsto manage dependencies. I use pip-tools as it provides a detailed requirements file outlining the source of each dependency installed in the project.(esd) esd/$ python -m pip install pip-tools -
Create a
requirements.inandrequirements-dev.infile for project and development dependencies respectively.(esd) esd/$ touch requirements.in requirements-dev.in -
Constrain the development dependencies with the main project dependencies to avoid dependency conflicts.
(esd) esd/$ echo -c requirements.txt >> requirements-dev.in -
Add the required development dependencies to
requirements-dev.in.(esd) esd/$ echo -e "pre-commit\nblack\nruff\nmypy\npytest" >> requirements-dev.in -
Add the required project dependencies to
requirements.in.(esd) esd/$ echo SQLAlchemy >> requirements.in -
Compile the requirements.txt and requirements-dev.txt files. Ensure to compile the requirements.txt first as requirements-dev.in will use this as the constraint file.
(esd) esd/$ pip-compile requirements.in (esd) esd/$ pip-compile requirements-dev.in -
Install dependencies within the virtual environment.
(esd) esd/$ python -m pip install -r requirements.txt -r requirements-dev.txt -
Create a
pyproject.tomlfile and configure development dependencies. I've included defaults from Ruff in thepyproject.tomlconfiguration to be explicit about settings.(esd) esd/$ touch pyproject.toml # pyproject.toml [tool.mypy] python_version = 3.11 strict = true pretty = true [[tool.mypy.overrides]] directories = "tests" # Allow untyped tests. [tool.black] line-length = 88 target-version = ['py311'] [tool.ruff] # Assume Python 3.11. target-version = "py311" select = [ "E", # pycodestyle "F", # Pyflakes "W", # pycodestyle warnings "C901", # McCabe complexity "N", # pep8-naming "D", # pydocstyle "UP", # pyupgrade "PL" # pylint ] ignore = ["D100", "D104"] # Allow autofix for all enabled rules (when `--fix`) is provided. fixable = ["ALL"] unfixable = [] # Exclude a variety of commonly ignored directories. exclude = [ ".bzr", ".direnv", ".eggs", ".git", ".git-rewrite", ".hg", ".mypy_cache", ".nox", ".pants.d", ".pytype", ".ruff_cache", ".svn", ".tox", ".venv", "__pypackages__", "_build", "buck-out", "build", "dist", "node_modules", "venv", ] per-file-ignores = {} # Same as Black. line-length = 88 # Allow unused variables when underscore-prefixed. dummy-variable-rgx = "^(_+|(_+[a-zA-Z0-9_]*[a-zA-Z0-9]+?))$" [tool.ruff.extend-per-file-ignores] "test_*.py" = [ "D101", # Missing docstring in public class "D102", # Missing docstring in public method "D103", # Missing docstring in public function ] "conftest.py" = [ "D101", # Missing docstring in public class "D102", # Missing docstring in public method "D103", # Missing docstring in public function ] [tool.ruff.mccabe] # Flag errors (`C901`) whenever the complexity level exceeds 10. max-complexity = 10 [tool.ruff.pydocstyle] # Use Google-style docstrings. convention = "google" [tool.pytest.ini_options] minversion = "6.0" addopts = "-ra -q" testpaths = [ "tests", ] # Placeholders for future configuration if required. [tool.ruff.isort] [tool.ruff.pep8-naming] [tool.ruff.pylint] [tool.ruff.pyupgrade] -
Create a
.pre-commit-config.yamlto configurepre-commit. Runningpre-commitbefore each git commit ensures code quality and consistency across the project.# .pre-commit-config.yaml repos: - repo: https://github.com/pre-commit/pre-commit-hooks rev: v4.4.0 hooks: - id: check-yaml - id: end-of-file-fixer - id: trailing-whitespace - repo: https://github.com/psf/black rev: 23.3.0 hooks: - id: black args: ['--config=./pyproject.toml'] - repo: https://github.com/charliermarsh/ruff-pre-commit rev: v0.0.276 hooks: - id: ruff - repo: https://github.com/pre-commit/mirrors-mypy rev: 'v1.4.1' hooks: - id: mypy args: [--no-strict-optional, --ignore-missing-imports] additional_dependencies: [ fastapi==0.99.1, sqlalchemy==2.0.17, typing-extensions==4.7.1 ] -
Use the
pre-commitautoupdate command to update hooks to the latest version and install the git hook scripts.(esd) esd/$ pre-commit autoupdate (esd) esd/$ pre-commit install -
Create a
.editorconfigfile to ensure consistency in formatting when collaborating with other developers.(esd) esd/$ touch .editorcongig # .editorconfig root = true [*] charset = utf-8 end_of_line = lf indent_style = space indent_size = 4 trim_trailing_whitespace = true insert_final_newline = true [*.html] indent_size = 2 -
Configure local settings for IDE. I currently use VSCode as my text editor/IDE.
(esd) esd/$ touch .vscode/settings.json # .vscode/settings.json { "python.formatting.provider": "black", "[python]": { "editor.formatOnSave": true, }, "editor.codeActionsOnSave": { "source.organizeImports": true }, "editor.rulers": [ 88, ], "python.analysis.typeCheckingMode": "strict", } -
Create project structure. I add
__init__.pyfiles in theesdandtestsdirectories to define them as packages.(esd) esd/$ mkdir esd tests && touch esd/__init__.py tests/__init__.py # Project tree after adding esd and tests directories esd ├── .venv ├── .vscode │ └──settings.json ├── esd │ └──__init__.py ├── tests │ └──__init__.py ├── .editorconfig ├── .gitignore ├── .pre-commit-config.yaml ├── pyproject.toml ├── requirements-dev.in ├── requirements-dev.txt ├── requirements.in └── requirements.txt -
Create a GitHub repository with
README.mdandLICENSEfiles.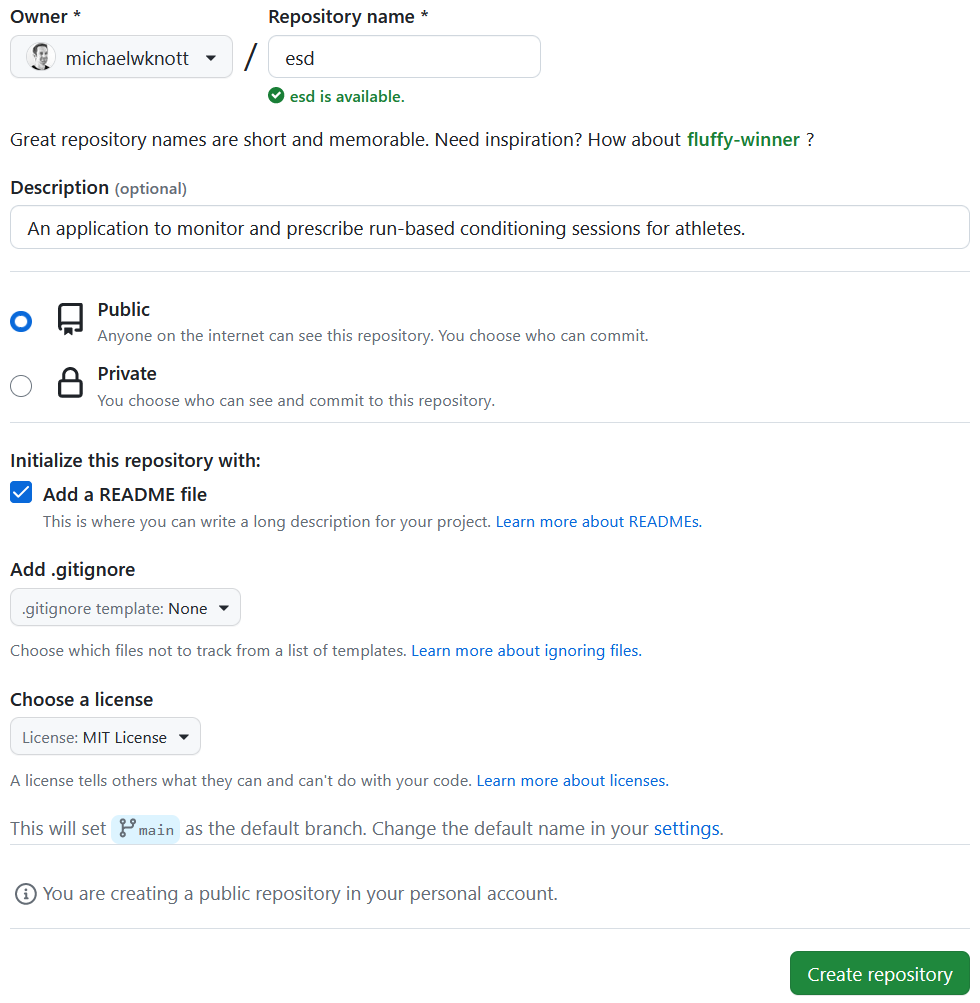
-
Link
esdproject to GitHub repository, add and commit project set-up changes and push changes to GitHub.# Add files to staging in local repo (esd) esd/$ git add . # Commit files in local repo (esd) esd/$ git commit -m "Project set-up" # Link local repository with remote repository on GitHub (esd) esd/$ git remote add origin git@github.com:michaelwknott/esd.git # Check the link between repositories has worked (esd) esd/$ git remote -v # Change the name of `master` to `main` (esd) esd/$ git branch -m main # Rebase local repository with the remote main branch. The local repository doesn't have `README.md` and `LICENSE` and needs these changes before pushing to the remote repository (esd) esd/$ git pull origin main --rebase # Push changes in local repository to GitHub (esd) esd/$ git push origin main -
The final project structure looks as follows:
esd ├── .venv ├── .vscode │ └──settings.json ├── esd │ └──__init__.py ├── tests │ └──__init__.py ├── .editorconfig ├── .gitignore ├── .pre-commit-config.yaml ├── LICENSE ├── README.md ├── pyproject.toml ├── requirements-dev.in ├── requirements-dev.txt ├── requirements.in └── requirements.txt